SEE ALSO:
BCL Webportal
Communicable Diseases
HIV
Mpox
NEED HELP?
Having trouble finding what you are looking for? Use our A to Z Index.
Congenital Syphilis Prevention
Alabama reported 36 cases of congenital syphilis in 2021, the highest number since 2006. The reported cases were more among women who received prenatal care than those who did not receive care. The most missed opportunities to prevent congenital syphilis among prenatal care recipients in Alabama were the lack of syphilis diagnosis in the early third trimester.
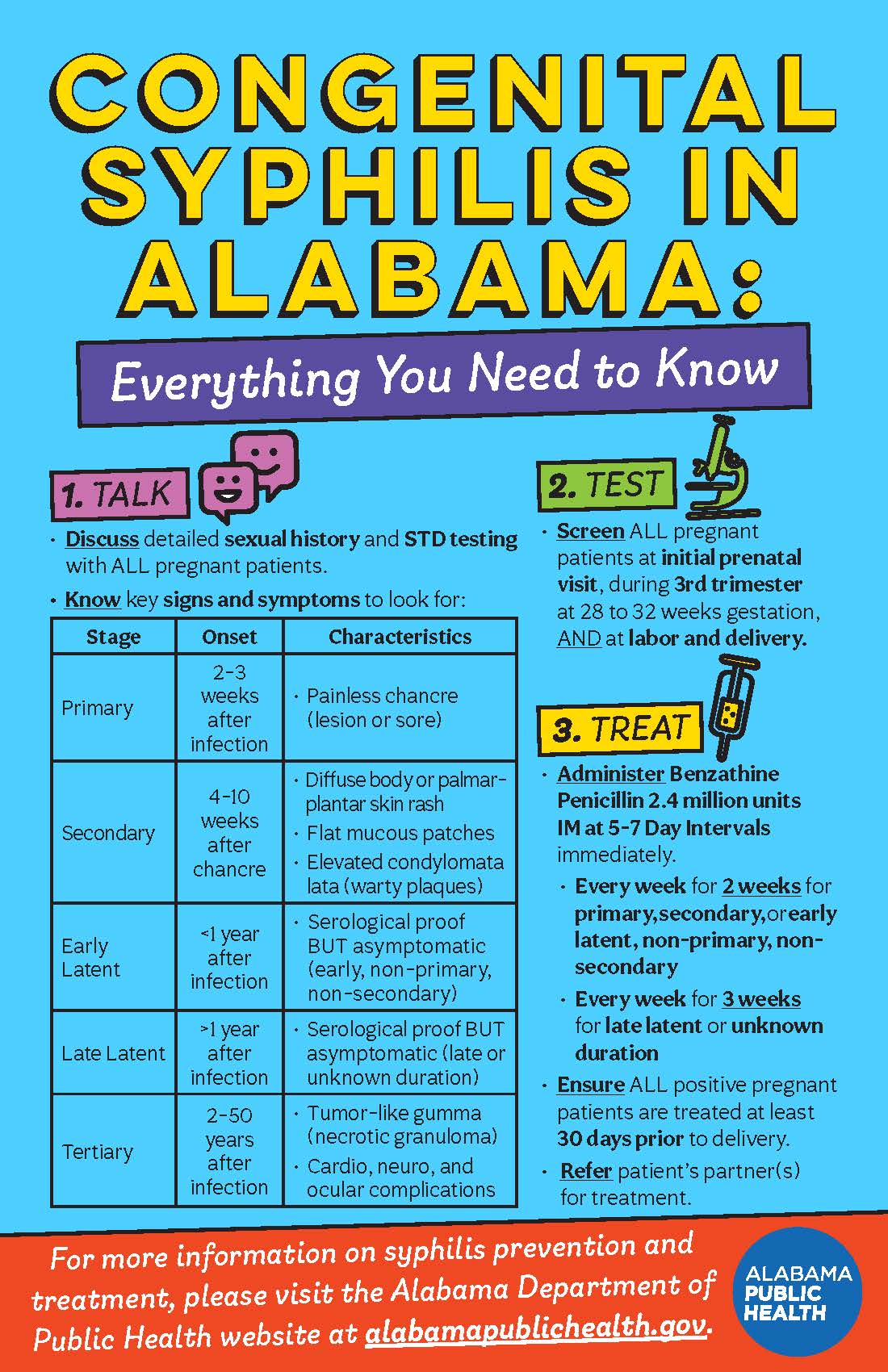 Congenital Syphilis in Alabama Fact Sheet
Congenital Syphilis in Alabama Fact Sheet
For a detailed look at the impact of congenital syphilis in Alabama, download our fact sheet.
Key Facts
- Women who are pregnant can become infected with the same STDs, including syphilis, as women who are not pregnant.
- Untreated syphilis in pregnancy can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, prematurity, low birth weight, or death shortly after birth.
- Women with a history of adequately treated syphilis before pregnancy may have babies with congenital syphilis.
- Babies born with congenital syphilis may have deformed bones; severe anemia; enlarged liver and spleen; jaundice; brain and nerve problems, such as blindness or deafness; meningitis; and skin rashes.
- In 2021, 62% of the missed opportunities to prevent congenital syphilis were provider-related because of late identification, inadequate treatment, or no syphilis testing during prenatal visits; 25% were unknown; and 15% were pregnant mother-related because of late or no prenatal care.
- For more information about syphilis and congenital syphilis cases, please visit cdc.gov/std.
ALPHTN Webcast: Syphillis and HIV in Pregnancy - Management of Infants
The following webcast provides information on the trends of syphilis and HIV in Alabama, the updated screening available for syphilis and HIV during pregnancy, and the management of a baby born to a mother with syphilis during pregnancy.
Recommended STD Treatment During Pregnancy
Newly Diagnosed Syphilis:
- Treat all pregnant women with a positive syphilis test or signs and systems of syphilis at least 30 days before delivery to prevent congenital syphilis.
- Primary Syphilis, Secondary Syphilis, or Early Non-Primary and Non-Secondary Syphilis: Benzathine penicillin 2.4 million units IM every week for two weeks at 5-7-day intervals.
- Syphilis Unknown Duration or Late Syphilis: Benzathine penicillin 2.4 million units IM every week for three weeks at 5-7-day intervals.
- Refer the patient’s partner for treatment to prevent reinfection of the pregnant woman.
History of Adequately and Inadequately Treated Syphilis
In 2019, four infants whose mothers were treated adequately for syphilis before pregnancy received the full congenital syphilis work-up. All four infants had significant abnormal lab findings and required treatment. These cases were reported to CDC as probable cases. Hence, the following is recommended as a preventive measure:
- Pregnant women with a history receive repeat treatment as Late Latent Syphilis with Benzathine penicillin 2.4 million units IM every week for three weeks at 5-7-day intervals.
Reactive Gonorrhea Test Results
- Person < 300 lb. Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM in a single dose.
- Person ≥ 300 lb. Ceftriaxone 1 g IM in a single dose.
- If Chlamydia Test Result is Positive - Add Azithromycin 1g orally in a single dose.
Reactive Chlamydia Test Results
- Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
ADPH Support
- ADPH offers free syphilis testing and treatment for pregnant women and their partners.
- Contact Dr. Agnes Oberkor, DrPH, at 334-206-3913 for help with determining syphilis history and the stage of syphilis infection.
Disease Reporting
- Report syphilis and congenital syphilis cases immediately online at epiweb.adph.state.al.us/redcap/surveys/?s=H37ENP8ADD or call ADPH STD Division at 334-206-5350.
Contact Us
- Mr. Anthony Merriweather, M.S.P.H.
334-206-2765 - Dr. Agnes Oberkor, DrPH
334-206-3913
Page last updated: February 4, 2026
SEE ALSO:
BCL Webportal
Communicable Diseases
HIV
Mpox
NEED HELP?
Having trouble finding what you are looking for? Use our A to Z Index.




